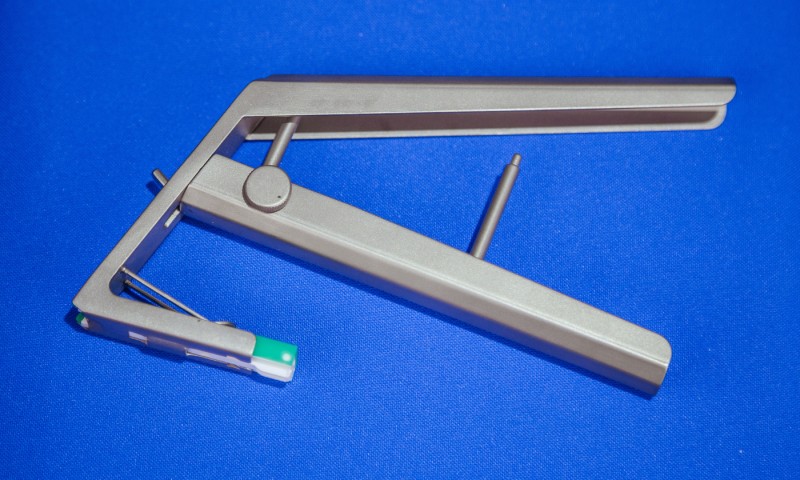
The Complete Guide To Using and Maintaining a Skin Stapler
A skin stapler is an important piece of equipment that medical professionals should thoroughly understand. Here’s a complete guide to using and maintaining one.
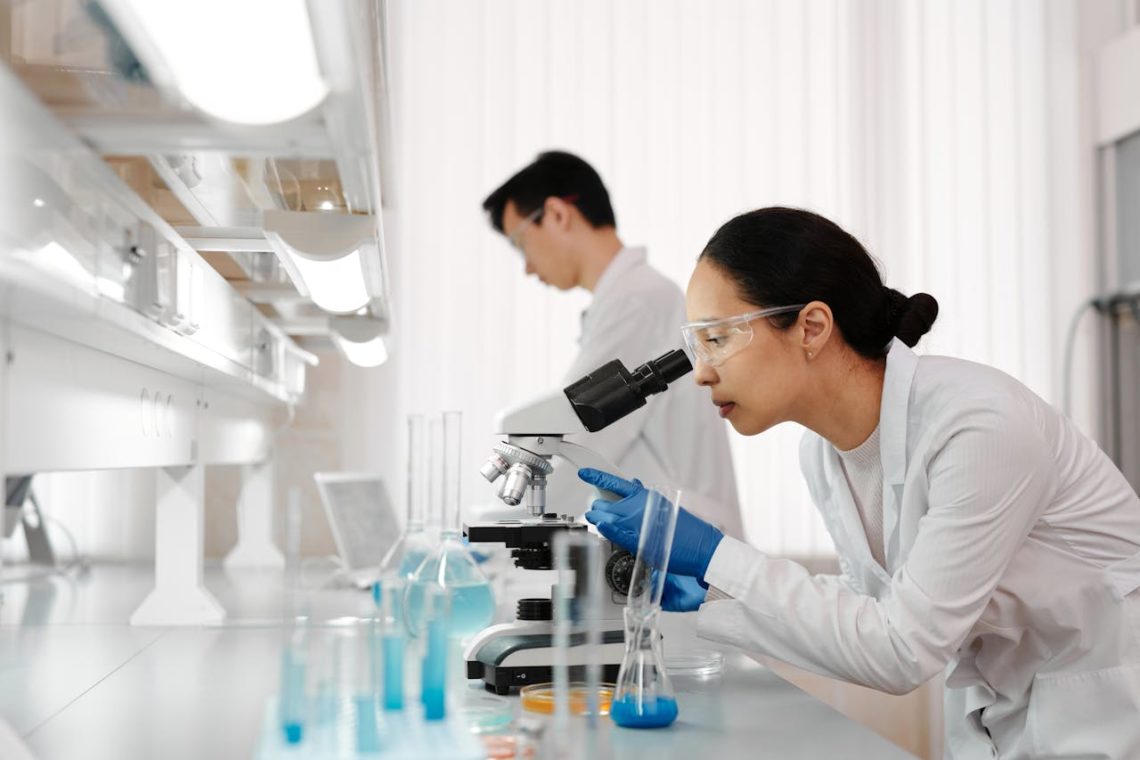
What Is an Automated Liquid Handling System in a Laboratory
Learn about the efficiency and precision of automated liquid handling systems in life science labs for accurate dispensing and increased productivity.
Nursing Career Advancement: Taking The Next Step
Unlock opportunities for nursing career advancement through strategic choices in continuous learning, specialization, mentorship, and networking. Elevate your path in the dynamic healthcare landscape for sustained growth and success.
How to Avoid Heavy Lifting Injuries (Useful Tips)
Learn how to avoid heavy lifting injuries. Follow proper lifting form, plan your path, and use lifting equipment. Prioritize safety over proving toughness and seek help when needed.
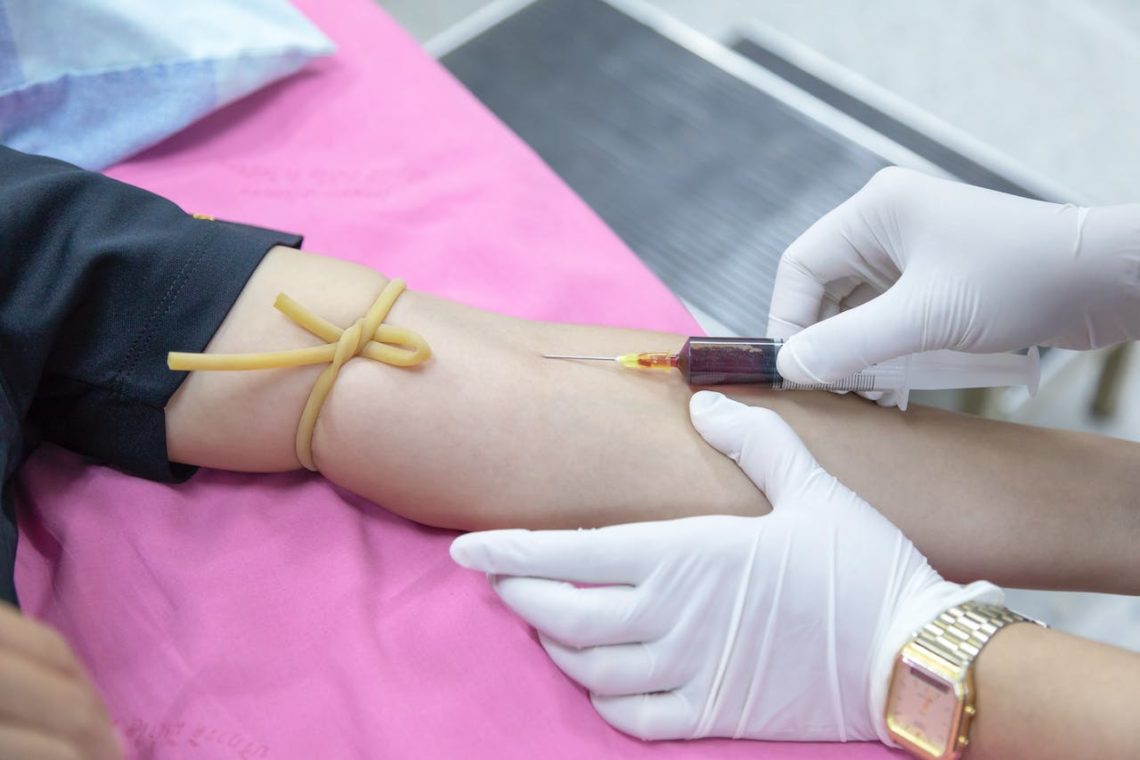
How Often Should You Get a Blood Test and What Does It Show
Unlock optimal health by learning how often you should get a blood test. Explore the significance of regular blood assessments for comprehensive well-being.
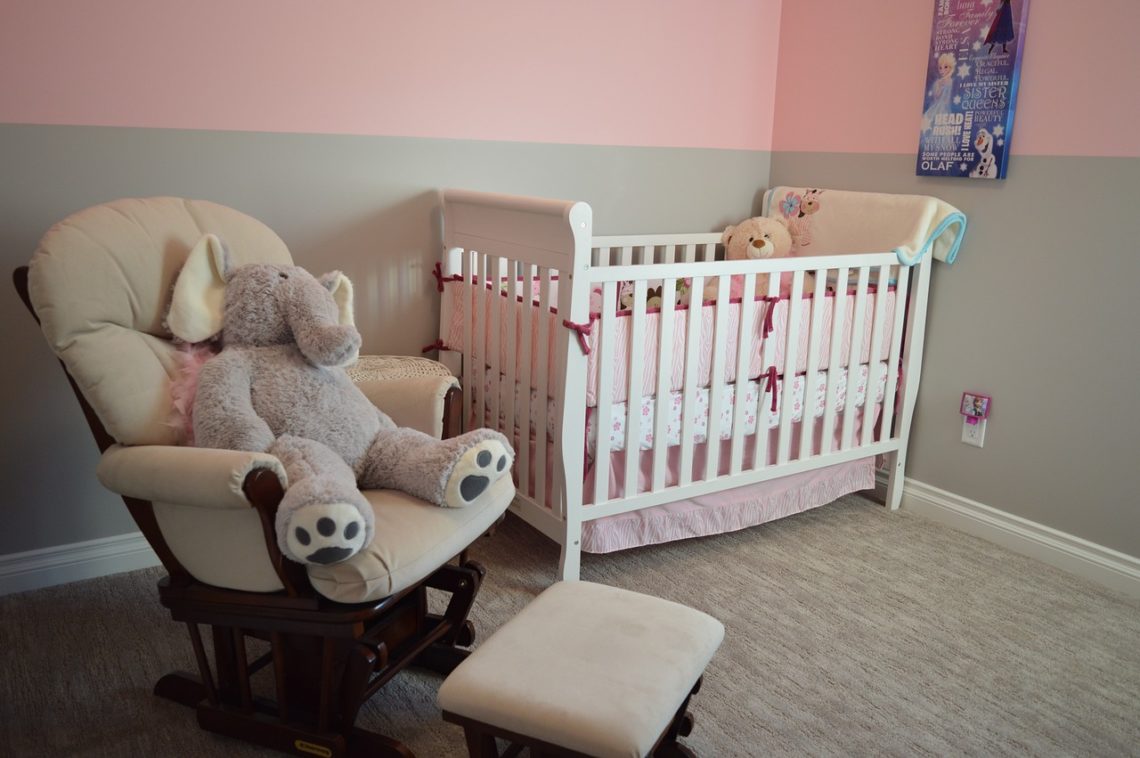
7 Gorgeous Baby Accessories to Add to Your Baby’s Nursery
Transform your baby's nursery into a haven with adorable and functional baby nursery accessories. From delightful mobiles to personalized wall letters, create a cozy haven for your little one.
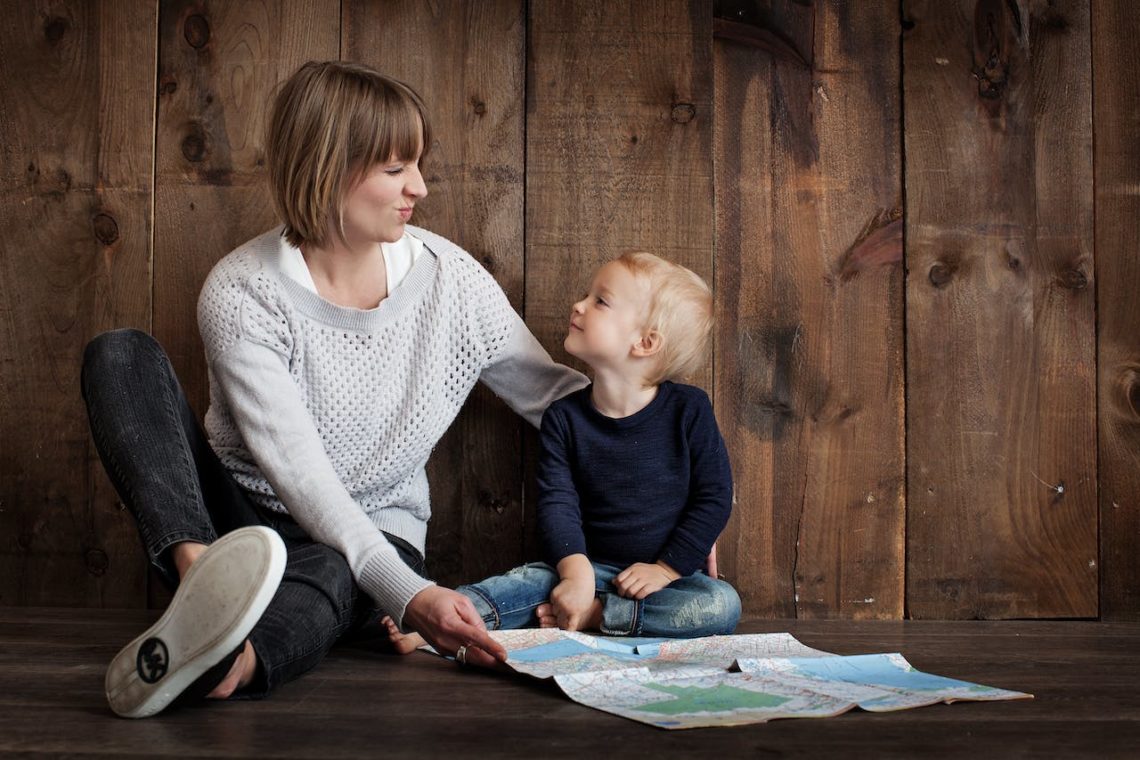
Proven Parenting Tips to Ensure Overall Growth of Your Child
Optimize your parenting journey to ensure overall growth of your child. Explore tips and strategies from education to emotional well-being for a well-rounded development approach.
How to Maintain Healthy Hair (In 15 Easy Tips)
Discover simple yet effective tips to maintain healthy hair effortlessly. From regular trims to protective measures, learn how mindful practices contribute to vibrant, strong hair.
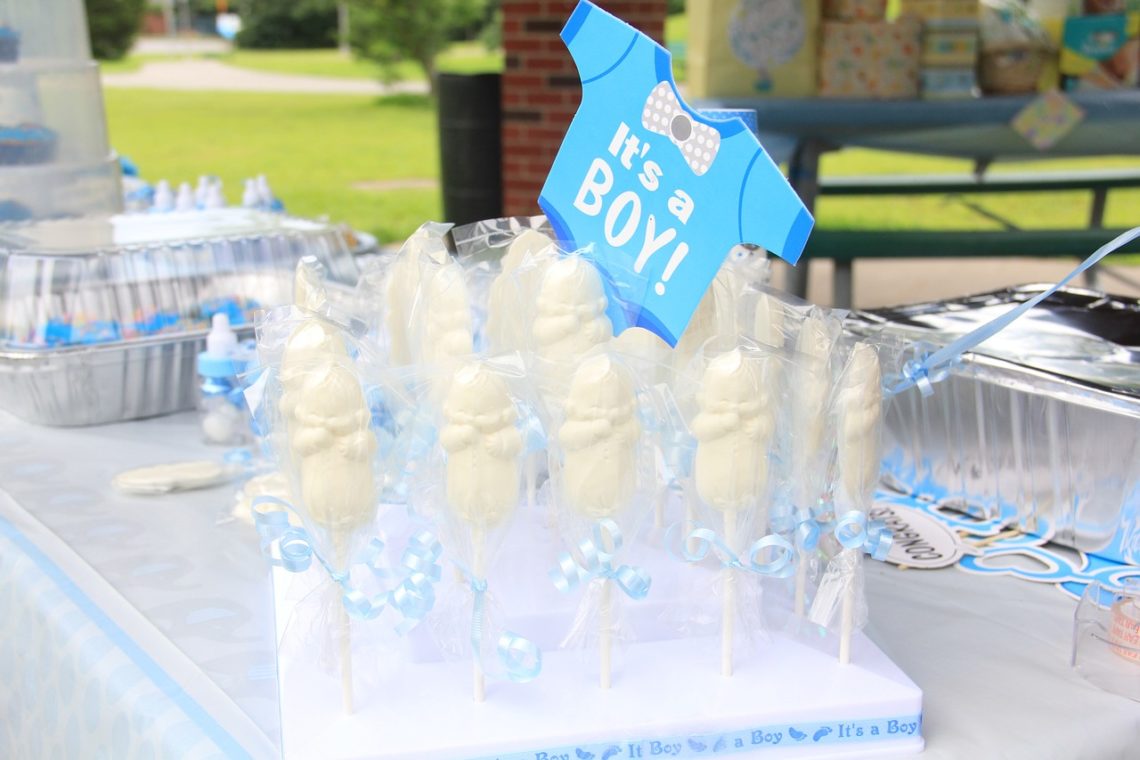
What Kind of Gifts to Offer During a Baby Shower
Discover the best baby shower gifts to celebrate the upcoming arrival! From cozy pajamas to essential nursery items, find the perfect gesture of love.
7 Ways to Help Your Body With Healthy Protein Sources
Explore diverse, healthy protein sources like Greek yogurt, lean meats, seafood, eggs, and legumes for a balanced and nourishing diet.
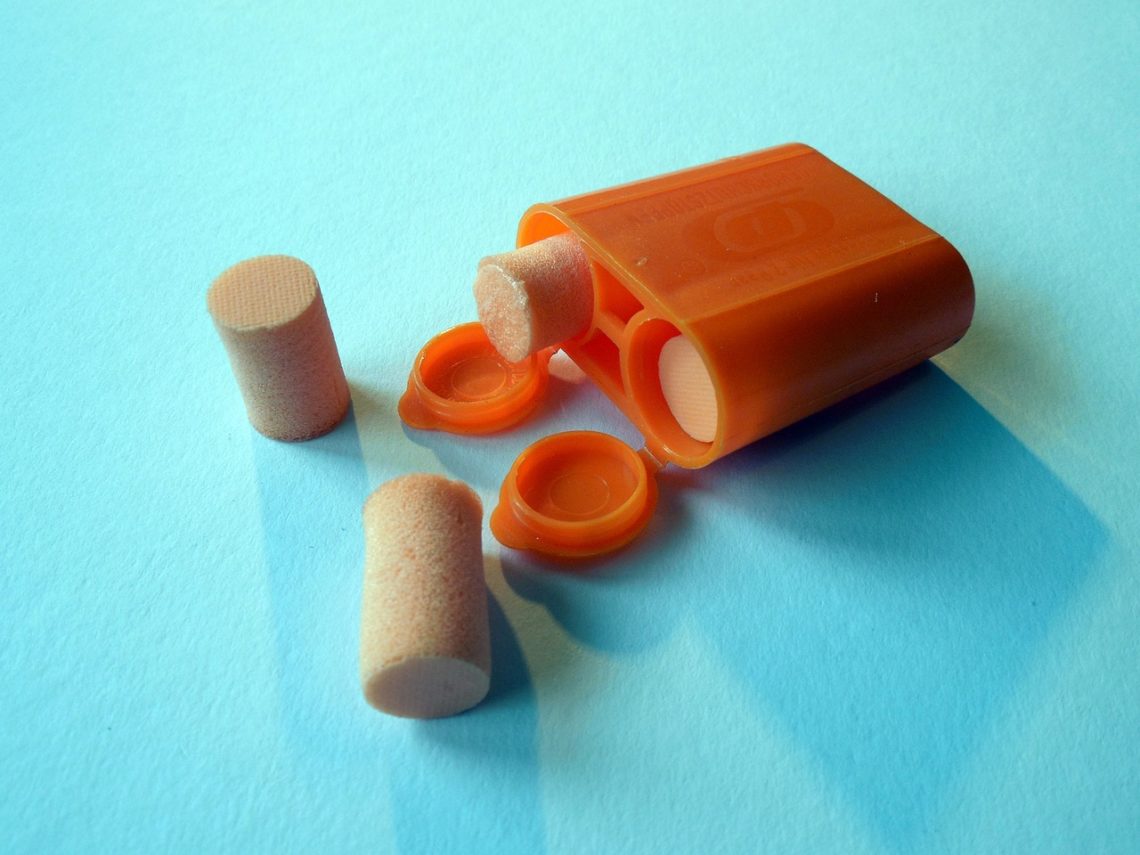
The Long-Term Health Benefits of Using Ear Plugs
Explore the benefits of ear plugs, from protecting hearing to improving sleep and concentration. Embrace tranquility with the versatile advantages of ear plugs.
How to Set Fitness Goals (In 6 Easy Steps)
Learn the art of achieving your fitness dreams with our guide on how to set fitness goals. Start your journey towards a healthier you today!